🦷 What Are Gum Diseases?
Gum sicknesses, regarded medically as periodontal diseases, have an effect on the tissues and bone that aid your tooth. They range from slight gum infection (gingivitis) to more excessive, damaging sickness (periodontitis) .
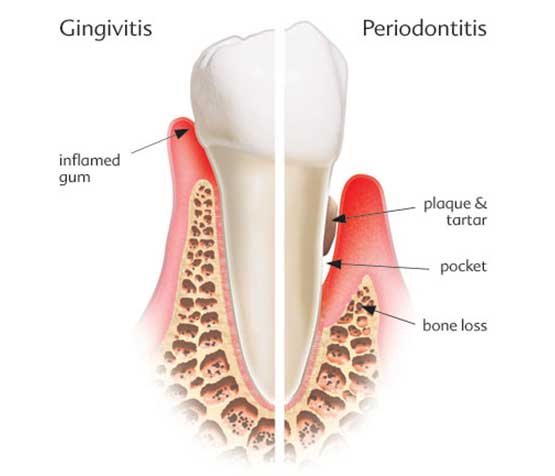
1. Gingivitis: The Early Stage
- Definition: Inflammation of the gums caused by a buildup of plaque—a sticky film of micro organism on enamel .
- Signs & Symptoms:
- Red, swollen gums that bleed without problems at some point of brushing or flossing .
- Possible terrible breath or metallic taste in the mouth
- Reversibility: Fully reversible with regular oral hygiene and normal professional cleanings .
2. Periodontitis: Advanced Gum Disease
When gingivitis is left untreated, it is able to development to periodontitis, which incorporates:
a) Mild to Moderate Periodontitis
- Formation of pockets among gums and teeth .
- Plaque and micro organism invade those wallet, main to bone loss .
- Gums may additionally recede, pus can also appear, and teeth can grow to be unfastened .
b) Severe/Advanced Periodontitis
- Significant bone destruction .
- Teeth loosen and can fall out .
- Treatment becomes more complex, from time to time requiring surgery .
3. Who Is at Risk?
- Primary cause: Poor oral hygiene main to plaque accumulation .
- Risk factors:
- Smoker: makes recuperation extra hard and hastens development .
- Diabetes and systemic sicknesses: boom susceptibility .
- Hormonal modifications (e.G., pregnancy), medicinal drugs, stress, genetics .
4. Why It Matters: Health Implications
- Globally, periodontal disease is a leading motive of adult enamel loss .
- Linked to extreme fitness conditions: heart ailment, stroke, diabetes complications, adverse pregnancy results, a few cancers .
- Chronic inflammation from gum disease may contribute to systemic health issues .
5. Diagnosis & Monitoring
- Dental tests involve probing gums, measuring pocket depths, and taking X‑rays to test bone loss .
- Regular dental visits (as a minimum every 6 months) are vital to seize troubles early, especially in case you’re at higher risk .
6. Treatment Options
For Gingivitis:
- Routine expert cleansing and improved oral hygiene behavior (brushing two times daily, flossing, mouthwash) .
For Periodontitis:
- Non‑surgical: Scaling and root planing, antibiotic rinses or gels, laser therapy .
- Surgical (for severe cases):
- Flap/pocket reduction, soft tissue grafts, bone regeneration, bone grafts, dental implants .
7. Prevention & Daily Care
- Brushing: Twice day by day for two minutes with a gentle-bristle fluoride toothpaste; update each 3–4 months .
- Flossing: Daily to put off plaque among tooth; interdental brushes or water flossers are effective options .
- Lifestyle: Quit smoking, manipulate pressure, hold balanced nutrition (nutrients A, C, D, calcium) .
- Professional care: Routine check-ups, professional cleanings, and well timed treatment .
📝 Summary Table
| Stage | Symptoms | Reversibility | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gingivitis | Red, swollen gums, bleeding | Yes | Cleaning, brushing, flossing |
| Mild ‑ Moderate | Pockets, bad breath, initial bone loss | No, but manageable | Scaling, root planing, antibiotics |
| Advanced | Loose teeth, significant bone loss | No | Surgical interventions, grafts |
Take-Home Message
Gum ailment often progresses silently—many human beings do not note signs and symptoms till harm is superior. Early detection thru ordinary dental check-united statescombined with constant oral care can prevent extreme consequences like tooth loss and systemic fitness issues. If your gums bleed or you are experiencing awful breath, swollen gums, or unfastened enamel, it’s time to seek advice from your dentist.