What is Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay (dental caries or cavities) is the destruction of the difficult tissues of teeth—teeth and dentin—via acids produced when positive micro organism in dental plaque metabolize sugars from food and drink . It’s one of the maximum substantial non-communicable illnesses globally, affecting almost three.6 billion people
Causes & Risk Factors
- Bacteria & Sugars: Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacilli thrive in plaque. They ferment sugars (sucrose, fructose, glucose), generating acid that demineralizes teeth
- Time & Frequency: Frequent sugar consumption maintains teeth beneath acid attack; plaque over time hardens into tartar.
- Host Factors: Tooth morphology (e.G., deep molar grooves), thinner teeth, low saliva float, fluoride deficits, and socioeconomic factors affecting hygiene behavior and get entry to to care.
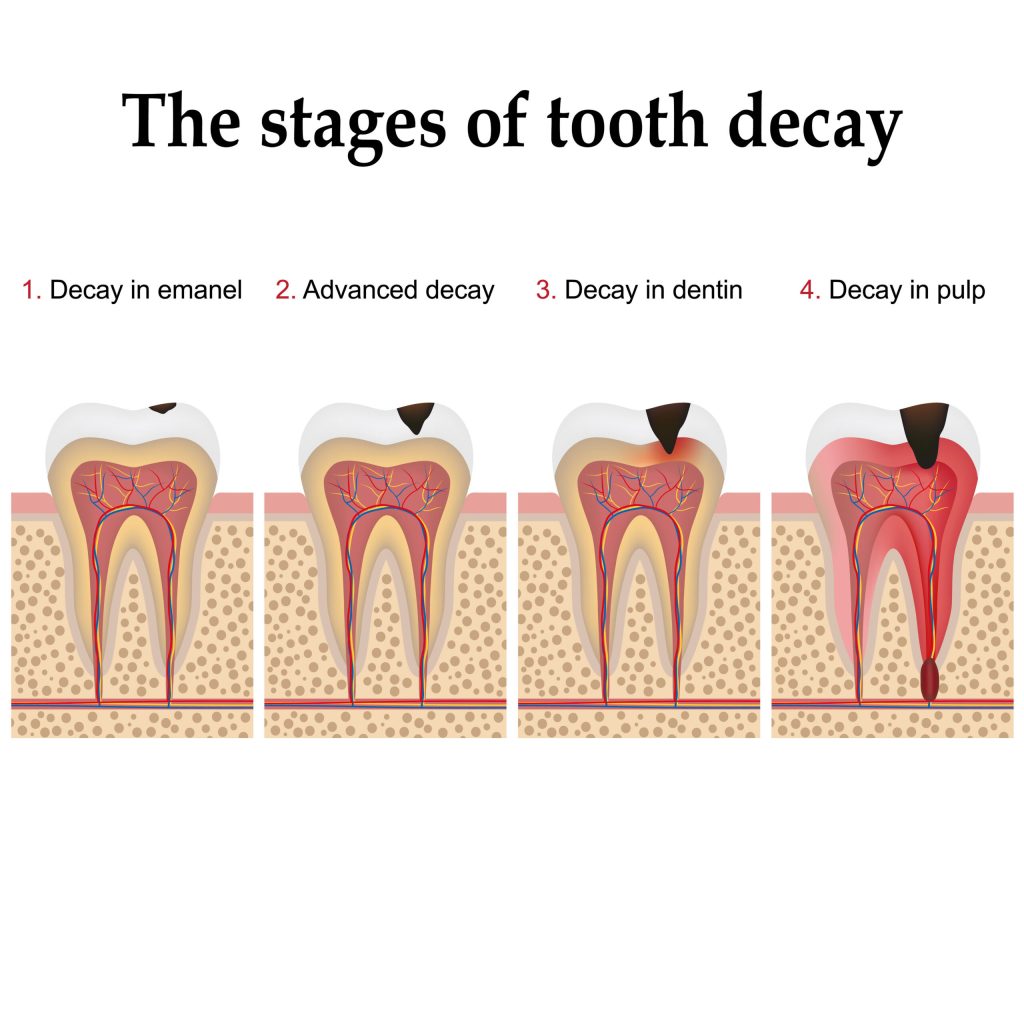
Stages of Tooth Decay
The manner commonly unfolds in five modern levels:
- Demineralization
Acid dissolves minerals from teeth, causing tiny white spots. At this stage, decay is reversible with fluoride .- Enamel Decay
Continued acid publicity ends in enamel breakdown and brown discoloration, resulting in cavities that require filling .- Dentin Decay
Once teeth is breached, decay spreads quicker into softer dentin, exposing tubules related to nerves and causing sensitivity- Pulp Damage
Infection reaches the pulp (nerves and blood vessels), triggering inflammation, pressure, and tooth pain- Abscess Formation
A bacterial infection at the pulp tip reasons pus, swelling, severe pain, and potentially dangerous unfold of infection .
Globally, untreated decay affects billions—over 2.4 billion adults and 621 million children
- Symptoms to Watch For
- White or brown spots on teeth surfaces
- Tooth sensitivity, especially with hot/bloodless or candy foods
- Persistent toothache or sharp pain
- Bad breath or foul flavor
- Swollen gums or facial swelling (in extreme cases)
Early decay is frequently symptom-loose, so everyday dental assessments and x-rays are critical
Diagnosis
Dentists diagnose decay through:
- Visual and tactile checks to discover softened regions or discoloration
- X-rays to discover hidden cavities between teeth or beneath fillings
Treatment Options
| Stage | Treatment |
| Initial demineralization | Fluoride varnishes or gels; day by day fluoride toothpaste and water fluoride to inspire tooth restore |
| Dentin decay | More great fillings or crowns to repair the enamel |
| Enamel decay (cavities) | Remove decay and fill the hollow space with composite, porcelain, or amalgam |
| Pulp harm | Root canal remedy to eliminate inflamed pulp, accompanied by a protecting crown |
| Abscess | Root canal or extraction; antibiotics can be needed to treat infection |
Prevention Strategies
- Oral hygiene: Brush two times each day with fluoride toothpaste, floss day by day, and use antimicrobial mouthwash to dispose of plaque
- Limit sugars: Reduce sugary, sticky snacks; avoid sugary drinks outside meals
- Fluoride publicity: Ensure fluoridated water, toothpaste, and expert remedies
- Dental sealants: Apply sealants to molars of children and teenagers to prevent decay in grooves
- Regular dental visits: Biannual checkups allow early detection and well timed intervention
- Support saliva fitness: Stay hydrated and don’t forget sugar-loose gum or cheese submit-meal to buffer acids
The Global Burden & Why It Matters
Tooth decay is a leading motive of ache, infection, and healthcare expenses. It leads to missed college or work and, in serious cases, systemic health issues . The WHO stresses sugar discount and fluoride as top prevention measures.
Bottom Line
Tooth decay is a preventable however full-size sickness pushed through micro organism, sugars, and time. Early stages can be reversed with right oral hygiene and fluoride. Once a cavity forms, dental treatment is essential. The handiest prevention lies in each day care, wholesome diet, fluoride use, sealants, and normal dental checkups.
Let me recognise in case you’d like a greater distinctive exploration of any topic or additional images!